Mar
17
2010
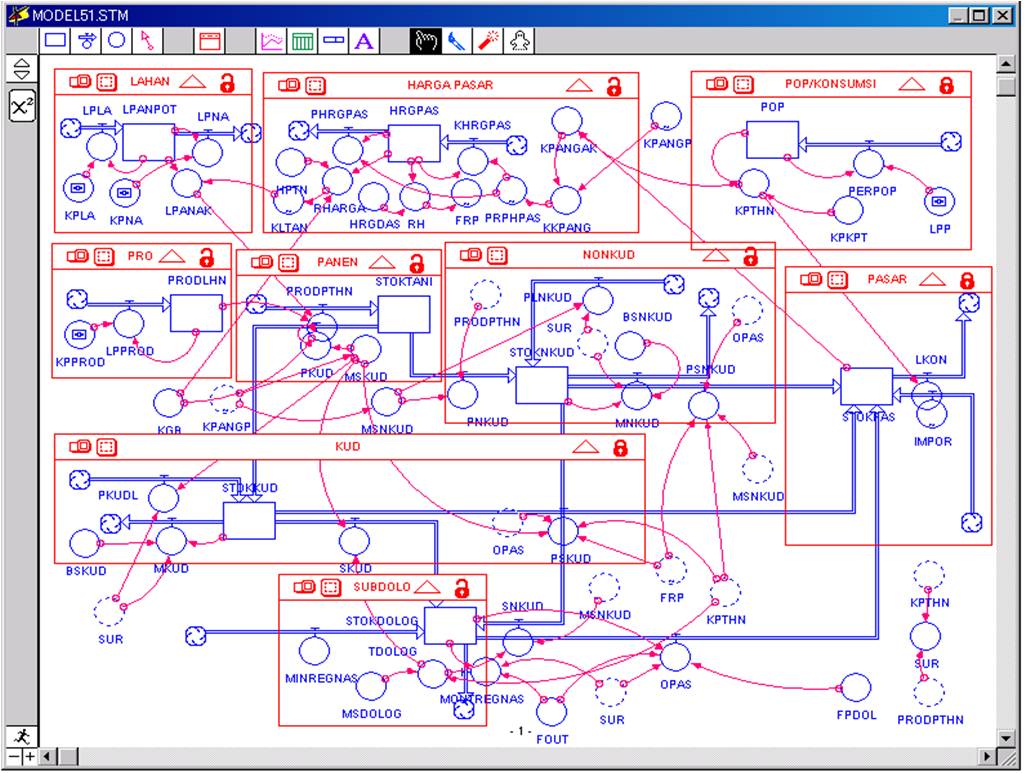 Indonesia is one of agricultural countries in the world that has significant role to endow with rich agricultural potentials. Furthermore, agricultural sector plays a big role in forming Gross National Income and also plays a role in supplying food and industrial raw materials. Refers to the Indonesian Government Policy, this sector can make an equal development through the endeavor of poverty reduction and the improvement of people’s income. The role of food supplier is to achieve food self-sufficiency. Therefore, there is a need to revitalize agriculture in a wider sense throughout Indonesia. One alternative to achieve the national target is innovating technology in agricultural production system.
Indonesia is one of agricultural countries in the world that has significant role to endow with rich agricultural potentials. Furthermore, agricultural sector plays a big role in forming Gross National Income and also plays a role in supplying food and industrial raw materials. Refers to the Indonesian Government Policy, this sector can make an equal development through the endeavor of poverty reduction and the improvement of people’s income. The role of food supplier is to achieve food self-sufficiency. Therefore, there is a need to revitalize agriculture in a wider sense throughout Indonesia. One alternative to achieve the national target is innovating technology in agricultural production system.
Related to the aforementioned, the study is focused on dynamic model development of System of Rice Intensification (SRI) for strengthening a food security in Indonesia. In general terms, the SRI is a method of increasing the yield of rice produced in farming system. This technology also improves productivity of land, labor, capital and water simultaneously. Recently, many methods of the SRI are being implemented in some countries with difference of circumstances and treatments.
Implementing the study was considered on some facts that particularly natural resources availability for agriculture will become scarce commodity in the future. Furthermore, demand for rice is increasing with population growth. Thus, any activities to increase rice productivity with less in-natural resource consumption will be important for sustainable food security. For developing the model, mechanism of the research can be described as follows; (i) identifying key variables and its behavior in the system, (ii) developing inter-relationship among key variables in the form of mathematical formulations, (iii) programming the model by using dynamic system based application software, and then simulating, (iv) validating the model to improve performance of the model.
The model was tested in some provinces, e.g. Yogyakarta, Central Java and East Java. For testing the model, three methods were compared i.e. organic SRI, inorganic SRI and conventional method. Results of the study indicated that the developed SRI model can improve significantly rice yield ranged 1.5 to 2 times compare to the conventional method.
Dec
11
2009
 The 10-th International Agricultural Engineering Conference was held in Asian Institute of Technology, Bangkok THAILAND from 7 – 10 December, 2009. The International Conference was organized by Asian Association for Agricultural Engineering (AAAE). The IAEC aimed to provide a forum for discussion and information transfer of current researches, achievements and practical application in all fields of agricultural engineering. The theme of this conference is “Role of Agricultural Engineering in Advent of Changing Global Landscape”. The related topics were arranged as agricultural engineering education, agricultural waste management, agro-industry and agri-business management, electronics in agriculture, energy in agriculture, ergonomics/human factors engineering, post harvest technology, food engineering and biotechnology, power and machinery, soil and water engineering, irrigation and drainage engineering, structures and environment, protected cultivation, terramechanics, new materials and other emerging technologies.
The 10-th International Agricultural Engineering Conference was held in Asian Institute of Technology, Bangkok THAILAND from 7 – 10 December, 2009. The International Conference was organized by Asian Association for Agricultural Engineering (AAAE). The IAEC aimed to provide a forum for discussion and information transfer of current researches, achievements and practical application in all fields of agricultural engineering. The theme of this conference is “Role of Agricultural Engineering in Advent of Changing Global Landscape”. The related topics were arranged as agricultural engineering education, agricultural waste management, agro-industry and agri-business management, electronics in agriculture, energy in agriculture, ergonomics/human factors engineering, post harvest technology, food engineering and biotechnology, power and machinery, soil and water engineering, irrigation and drainage engineering, structures and environment, protected cultivation, terramechanics, new materials and other emerging technologies.
The author has presented his research paper titled “Design of Control System for Silk Worm’s Growth Chamber to Improve the Quality of Raw-Silk” that prepared together with Mr. Atris Suyantohadi, Mr. Hari Purwanto and Mr. Radi. Special thanks to Universitas Gadjah Mada for supporting us to participate in this conference.
Nov
27
2009
 Nowadays, demand for integrating between information technology (IT) and development of agricultural system is in order to increase the productivity, efficiency and profitability in term of precision agriculture. This matter occurred due to some problems in the field, such as; unintensively monitoring activities for plant during the growing period. One of the alternative solutions to overcome the problem was introducing the machine vision technology in the farming system. The research is actually as a basic research that aims using technology of digital image processing and software of computation (mathematics) to support a function of real-time monitoring system for plant growing. The research mechanism was started from digital image processing by using an image segmentation method that can identify between the main object (plant) and others (soil, weed). The next was to calculate and analyze a percentage of the plant growing, from after planting until harvesting time. The analyzed data were stored as MySQL database format in the web server. Final output of the research was the web based monitoring instruments for plant growing that can be accessed through intranet (local network) as well as internet technology.
Nowadays, demand for integrating between information technology (IT) and development of agricultural system is in order to increase the productivity, efficiency and profitability in term of precision agriculture. This matter occurred due to some problems in the field, such as; unintensively monitoring activities for plant during the growing period. One of the alternative solutions to overcome the problem was introducing the machine vision technology in the farming system. The research is actually as a basic research that aims using technology of digital image processing and software of computation (mathematics) to support a function of real-time monitoring system for plant growing. The research mechanism was started from digital image processing by using an image segmentation method that can identify between the main object (plant) and others (soil, weed). The next was to calculate and analyze a percentage of the plant growing, from after planting until harvesting time. The analyzed data were stored as MySQL database format in the web server. Final output of the research was the web based monitoring instruments for plant growing that can be accessed through intranet (local network) as well as internet technology.
Sep
09
2009
 Recently, the main challenge in the development of agricultural industry sector is the limited presence of the natural resources of agriculture, both in quantity and quality aspects. One of the natural resources that significantly degrade is an agricultural land area. The research was conducted for identifying the capacity of coastal area as one of the natural resources to support development of an agro-industry through introducing agricultural innovation technology. In this stage, outputs of the research were an information system for managing those innovation technologies and profile of the farming system in coastal area.
Recently, the main challenge in the development of agricultural industry sector is the limited presence of the natural resources of agriculture, both in quantity and quality aspects. One of the natural resources that significantly degrade is an agricultural land area. The research was conducted for identifying the capacity of coastal area as one of the natural resources to support development of an agro-industry through introducing agricultural innovation technology. In this stage, outputs of the research were an information system for managing those innovation technologies and profile of the farming system in coastal area.
Research mechanisms include: (i) identification of system parameters through field observations, (ii) preparation of model development system, (iii) development of software-based GIS, (iv) validation and verification of systems with field data acquisition, and (v) standardization system. The developed model was tested in three districts in Province Yogyakarta, namely (i) Bantul, (ii) Kulon Progo and (iii) Gunungkidul. (published by Journal of Agritech 30(2) 2010 – Universitas Gadjah Mada)
Sep
04
2009
 The second part of the study was to validate the developed information system in a selected farming area. For the primary data, a farm survey was conducted in Sleman Regency, Yogyakarta Province. The sixty (60) household farms in 6 (six) districts were investigated which were grouped into animal based and tractor based farms.
The second part of the study was to validate the developed information system in a selected farming area. For the primary data, a farm survey was conducted in Sleman Regency, Yogyakarta Province. The sixty (60) household farms in 6 (six) districts were investigated which were grouped into animal based and tractor based farms.
Based on the farm survey, the results described that the total annual water surplus in the study area was 792 mm that reached from November to April and water deficit was 355 mm from May to October. There is also surplus situation of number of animal drawn and local equipment for land preparation in each district, but deficiency in number of power tiller and it’s matching tillage equipment. The sensitivity analysis indicated those yield and crop price are the most significant factor in determining the net return of the crop production system.
Sep
04
2009
 This study was undertaken to develop a computer program package for identifying a farming system that was focused in the water availability analysis, the optimizing of agricultural power and selected equipment and the sensitivity analysis. The computer programs for all models were developed and written in FoxBASE command language. Three databases were obtained from the farm survey i.e.; climate, crop and power. All these databases can be appended, edited, deleted or displayed by the users through a menu of database management system (DBMS). They were used to evaluate the utility of the computer programs as input data. The information system calculates the amount of monthly water surplus and deficit, the optimum number of agricultural power (animal or power tiller) and its matching implement required and also change in the net return of crop production system due to the change of input variables such as crop price, yield, and production material cost. The system output for each analysis can be presented in three options by screen, printer and file that can be accessed to another language.
This study was undertaken to develop a computer program package for identifying a farming system that was focused in the water availability analysis, the optimizing of agricultural power and selected equipment and the sensitivity analysis. The computer programs for all models were developed and written in FoxBASE command language. Three databases were obtained from the farm survey i.e.; climate, crop and power. All these databases can be appended, edited, deleted or displayed by the users through a menu of database management system (DBMS). They were used to evaluate the utility of the computer programs as input data. The information system calculates the amount of monthly water surplus and deficit, the optimum number of agricultural power (animal or power tiller) and its matching implement required and also change in the net return of crop production system due to the change of input variables such as crop price, yield, and production material cost. The system output for each analysis can be presented in three options by screen, printer and file that can be accessed to another language.
Sep
04
2009
 A control method for autonomous vehicles was developed to steer the vehicle to a given goal point. Since four wheeled vehicles have constraints known as non-holonomic constraints, a nonlinear control theory was applied to generate a trajectory that would permit a vehicle to run from a starting point to the goal within these constraints by tracking it.
A control method for autonomous vehicles was developed to steer the vehicle to a given goal point. Since four wheeled vehicles have constraints known as non-holonomic constraints, a nonlinear control theory was applied to generate a trajectory that would permit a vehicle to run from a starting point to the goal within these constraints by tracking it.
In this study, the trajectory control algorithm was applied to automatic fertilizer refilling with an autonomous vehicle equipped with a broadcast fertilizer distributor. Since the proposed control algorithm was an open-loop control, disturbances such as slippage of wheels caused navigation error.
To minimize error, feedback terms were added by linearizing the vehicle’s kinematic equations around a nominal trajectory generated with the open-loop algorithm. A fan beam type laser sensor was used for finding and positioning a fertilizer supplier on which light reflectors were attached for positioning. The accuracy of the control was examined by simulation and field experiments.
The field experiments were repeated by changing postures of the autonomous vehicle with the container at the start point. Results of the field experiment showed that the algorithm could guide the vehicle with satisfactory accuracy for refilling. The main factor in navigation error was limitation in the steering angle of the front wheels.(funded by : Ph.D Program Dissertation – Monbusho Japan 1997-2001 – supervised by : Prof. Tomohiro TAKIGAWA)
Sep
02
2009
 Sleman, as an area with rapid economic growth, against the challenge of development in relation with population expansion, local autonomy and good governance. In one hand, there is lack of synergy among development stakeholders, on the other hand information is ineffectively used during the decision making process. This paper aimed to develop a model of rural development plan based on agricultural sector using two computer softwares, i.e: (i) Geographical Information System (GIS) as spatial information system and (ii) Powersim to program the dynamic system behavior.
Sleman, as an area with rapid economic growth, against the challenge of development in relation with population expansion, local autonomy and good governance. In one hand, there is lack of synergy among development stakeholders, on the other hand information is ineffectively used during the decision making process. This paper aimed to develop a model of rural development plan based on agricultural sector using two computer softwares, i.e: (i) Geographical Information System (GIS) as spatial information system and (ii) Powersim to program the dynamic system behavior.
The model provides information on existing condition and consists of five components namely geography, development function, infrastructure, institution, and data catalog. The model was developed through formulating causal diagrams of development sectors and set it in a dynamic programming. The model was then validated in Moyudan, Sleman for the case of agriculture development, which is showed that the model was valid. (published by : Journal of Agritech, Fac. of Agricultural Technology UGM, Vol. 25 No. 1 2005 – co-authors : Sigit Supadmo A. and Murtiningrum).
Sep
02
2009
 The world demand of raw-silk provides a great opportunity to the development of raw-silk production in Yogyakarta. Recently, only 21% out of the overall world demand of raw-silk is fulfilled, whereas Indonesia contributes only 0.1% per year. The main problem is the lack of quality of raw-silk.
The world demand of raw-silk provides a great opportunity to the development of raw-silk production in Yogyakarta. Recently, only 21% out of the overall world demand of raw-silk is fulfilled, whereas Indonesia contributes only 0.1% per year. The main problem is the lack of quality of raw-silk.
The optimum growth of silkworm depends on micro environments, i.e. temperature, humidity, aeration, and light intensity. The research was aimed, to apply an automated “on/off” control technology in the silkworm rearing environmental monitoring. The result expected is high-grade quality of cocoon. In the research, two different conditions of silkworm growing environments were compared: controlled environment (in the rearing box) and normal environment. Then, from third instar (silkworm`s growth stage) to cocoon`s stage (final stage or fifth instar), temperature and air humidty were set on 240C – 260C and 70% – 80% respectively. While, Aeration and light intensity were ranged 0.1 – 0.3 m/s and 15 – 30 lux for all instar stages (constant) respectively.
The result indicated that there was an increasing the percentage of cocoon skin’s grade in the controlled rearing environment (19.66%), compared to the result of normal rearing environment (18.56%), also there was significantly different result on the thickness of the cocoon produced. (published by : Journal of Agritech, Fac. of Agricultural Technology UGM, Vol. 24 No. 4 2004 – co-authors : Atris Suyantohadi, Hari Purwanto, Radi)
Aug
19
2009
 The control of an autonomous agricultural vehicle operating on unstructured changing terrain includes many objective difficulties. One major difficulty concerns the characteristics of the terrain condition that the vehicle should operate in. Problems can range from the effects of varying terrain conditions on the autonomous vehicle sensors and traction performance through to the need to deal with the presence of unexpected situations.
The control of an autonomous agricultural vehicle operating on unstructured changing terrain includes many objective difficulties. One major difficulty concerns the characteristics of the terrain condition that the vehicle should operate in. Problems can range from the effects of varying terrain conditions on the autonomous vehicle sensors and traction performance through to the need to deal with the presence of unexpected situations.
On unstructured changing terrain, many factors influence vehicle behavior such as terrain slope, lateral slippage, and so on. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a more suitable model for vehicle motion on these terrain conditions. In order to control the vehicle along a course on unstructured changing terrain, it will be developed control software to enable more accurate control.
In this research, we will introduce the difficulty vehicle are facing in unstructured changing terrain and how learning and computational intelligence can help the vehicle to adapt and give them the necessary intelligence they to face the challenges they encounter in their conditions. The developed method to control the vehicle when operating on these conditions is Neuro-Fuzzy Controller.
Neuro-Fuzzy sets and systems constitute one of the most fundamental and influential computational intelligence tools. Given the uncertain and incomplete information an autonomous vehicle has about the condition, neuro-fuzzy rules provide an attractive means for mapping sensor data to appropriate control actions in real time. The success of Neuro-Fuzzy Logic Control (NFLC) is owed in a large part to the technology’s ability to convert qualitative linguistic descriptions into complex mathematical functions and the ability to deal with various situations without analytical model of the environment. The methodology of the NFLC appears very useful when the processes are too complex for analysis by conventional quantitative techniques or when the available sources of information are interpreted qualitatively, inexactly or uncertainly.
The neuro-fuzzy controller is based on the fuzzy membership function-based neural networks (FMFNN) with advantages of fuzzy logic and neural networks, such as inference capability and adoption of human operators, experience with fuzzy logic, and universal approximation and learning capability with neural networks.(funded by : Follow-up Research Program – JASSO Japan 2008/2009 – supervised by : Prof. Tomohiro TAKIGAWA)
 Indonesia is one of agricultural countries in the world that has significant role to endow with rich agricultural potentials. Furthermore, agricultural sector plays a big role in forming Gross National Income and also plays a role in supplying food and industrial raw materials. Refers to the Indonesian Government Policy, this sector can make an equal development through the endeavor of poverty reduction and the improvement of people’s income. The role of food supplier is to achieve food self-sufficiency. Therefore, there is a need to revitalize agriculture in a wider sense throughout Indonesia. One alternative to achieve the national target is innovating technology in agricultural production system.
Indonesia is one of agricultural countries in the world that has significant role to endow with rich agricultural potentials. Furthermore, agricultural sector plays a big role in forming Gross National Income and also plays a role in supplying food and industrial raw materials. Refers to the Indonesian Government Policy, this sector can make an equal development through the endeavor of poverty reduction and the improvement of people’s income. The role of food supplier is to achieve food self-sufficiency. Therefore, there is a need to revitalize agriculture in a wider sense throughout Indonesia. One alternative to achieve the national target is innovating technology in agricultural production system.







